Acrodermatitis Enteropathica (AE) is a rare inherited or acquired disorder that results from zinc deficiency. It primarily affects the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and immune system. Here’s a comprehensive overview:
Acrodermatitis Enteropathica is a zinc absorption disorder, either genetic or acquired, characterized by:
Eczematous or vesiculobullous skin lesions
Diarrhea
Hair loss (alopecia)
Irritability and growth retardation (especially in infants and children)
🧬 Types:
Congenital (Hereditary) AE:
Autosomal recessive disorder.
Caused by mutation in the SLC39A4 gene, which encodes a zinc transporter protein (ZIP4).
Symptoms appear shortly after weaning from breast milk (usually in infancy).
Acquired AE:
Seen in premature infants, alcoholics, people with malabsorption syndromes, parenteral nutrition, or vegetarian diets.
Can occur at any age.
🧍♂️ Symptoms:
Skin:
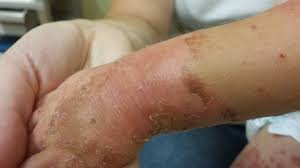
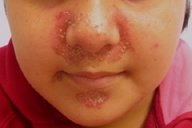
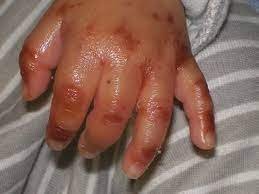
Red, inflamed, crusted lesions typically around:
Mouth (perioral area)
Eyes (periorbital area)
Genital and anal region
Hands and feet
Hair:
Thinning or complete hair loss (alopecia)
GI Symptoms:
Chronic diarrhea
Poor appetite
Other:
Irritability
Growth failure
Increased susceptibility to infections (especially fungal and bacterial)
🔍 Diagnosis:
Clinical features + Lab tests:
Low serum zinc levels
Low alkaline phosphatase levels (zinc-dependent enzyme)
Genetic testing (for SLC39A4 mutations) confirms congenital AE.
Skin biopsy: Nonspecific but may show psoriasiform or spongiotic dermatitis.
💊 Treatment:
Zinc supplementation:
Lifelong oral zinc (usually 1-3 mg/kg/day of elemental zinc).
Dramatic improvement of symptoms within days of starting zinc.
Monitor zinc levels regularly, especially in congenital cases.
🩺 Prognosis:
Excellent with early diagnosis and continuous treatment.
Delay in treatment can lead to serious infections, growth issues, and developmental delays.
📌 Key Points to Remember:
| Feature | Congenital AE | Acquired AE |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Genetic mutation (SLC39A4) | Inadequate zinc intake/absorption |
| Onset | Infancy (after weaning) | Any age |
| Treatment | Lifelong zinc supplementation | Zinc supplementation as needed |
| Prognosis | Excellent with treatment | Good with correction of cause |
